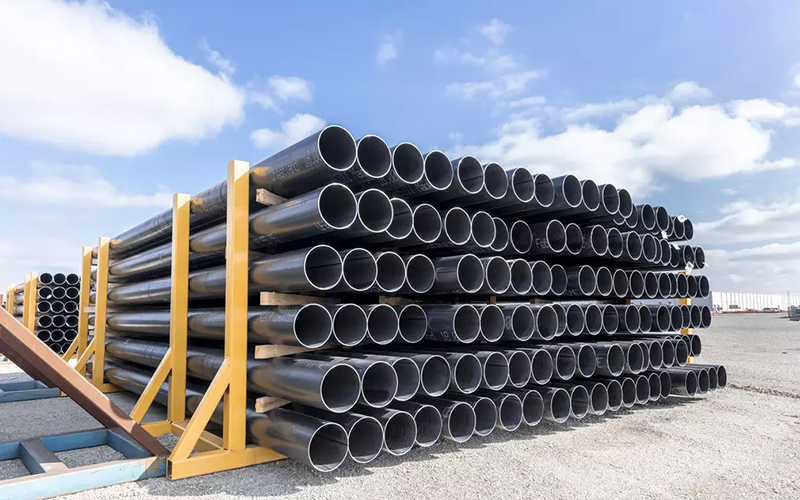
ERW Pipe
-
Type: High-frequency ERW pipe & API 5L ERW pipe
-
Size Range: 1/2″–24″ OD, 1.8–16 mm WT
-
Standards: API 5L, ASTM A53, ASTM A135, EN 10219
-
Advantages: Lower cost than seamless, tight tolerances, easy welding
ERW pipe (Electric Resistance Welded pipe) is a welded steel pipe manufactured from flat steel strip or coil, which is formed into a cylindrical shape and welded longitudinally by high-frequency electric resistance welding. The weld is created by heating the strip edges with electric current and forging them together under pressure, without the use of filler metal. The ERW pipe meaning in purchasing language is a straight-seam, longitudinally welded pipe made from strip/coil by electric resistance welding. The ERW pipe definition and meaning of ERW pipe align to the same product form: an ERW welded pipe (often written as ERW steel pipe) with a controlled weld seam and consistent geometry for code-permitted services. In procurement documents, ERW meaning for pipe is typically expressed by the governing standard, grade, size expression (NPS/Schedule or OD/WT), and the weld seam testing scope that closes acceptance. In practice, what are ERW pipes: they are the high-output welded pipe option selected when specifications allow welded construction with verifiable weld seam control. In modern production, ERW pipe typically refers to high-frequency ERW pipe (HF-ERW or HFI welded pipe), which offers stable weld quality, consistent dimensions, and high manufacturing efficiency for standard pipe sizes.
ERW Pipe vs Seamless Pipe – Basic Understanding
Compared with seamless pipe in the same diameter range, ERW pipe is produced from steel coil and benefits from: More uniform wall thickness control, Tighter outside diameter tolerances, Higher production efficiency, Lower material and manufacturing cost. For many low to medium pressure applications, ERW pipe fully meets design and code requirements while offering a more economical solution than seamless pipe. The phrase seamless ERW pipe appears in enquiries, but it is not a standard product category: ERW is welded pipe with a longitudinal seam, while seamless pipe has no seam. This is why comparisons are commonly framed as ERW pipe vs seamless, seamless pipe vs ERW pipe, or seamless pipe vs welded pipe—the commercial decision is driven by service severity, inspection scope, and the governing specification rather than by naming shortcuts.
| Service / Condition | Preferred Pipe Type | Engineering & Cost Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Onshore pipelines within moderate pressure and temperature (API 5L gathering and transmission lines) | ERW Pipe | Stable wall thickness, consistent OD, reliable weld performance, and clear cost advantage for standard onshore applications. |
| Water, gas and low-pressure fluid service (utilities, fire protection, cooling water) | ERW Pipe | Meets code requirements for low and medium pressure duties and avoids unnecessary seamless cost in non-critical services. |
| Structural and mechanical applications (supports, frames, racks) | ERW Structural Pipe | Excellent dimensional control and straightness for static load-bearing structures with economical sourcing. |
| Standard pipe sizes up to approx. 24″ OD | ERW Pipe | Coil-based HF-ERW enables high output, shorter lead time, and lower unit cost for bulk project sizes. |
| High-temperature or very high-pressure services (boiler tubes, critical steam lines) | Seamless Pipe | More suitable for extreme pressure/temperature conditions where codes require additional safety margin. |
| Severe sour service or fatigue-critical conditions (H₂S environments, cyclic loading) | Seamless Pipe | Often required by project specifications to reduce risk under sour service or high cyclic stress conditions. |
Practical engineering selection rule Prefer ERW Pipe where allowed Use ERW pipe wherever codes and client specifications permit, reserving seamless pipe only for genuinely critical services to optimize total project cost.
ERW pipe pressure rating is not a single fixed value tied to the manufacturing label. Pressure capability is determined by the governing design code and inputs such as OD, wall thickness (schedule), grade/strength level, temperature derating, corrosion allowance, and the code factors used for the design check. For procurement alignment, the controllable “order-able” elements are the ERW pipe specification fields (standard, grade, size expression, testing scope, and documentation), which together support a pressure design verification under the project code.
ERW Pipe Supplied by Octal Steel
Octal Steel supplies ERW pipe and API 5L ERW line pipe from qualified and audited mills, covering international standards for fluid service, line pipe, and structural use.
Typical supply scope of ERW pipe:
• Outside Diameter: approx. 1/2″–24″ (21.3–610 mm)
• Wall Thickness: approx. 1.8–16 mm, depending on size and standard
• Length: 6–12 m (SRL / DRL) or fixed lengths on request
• Pipe Type: High-frequency ERW pipe (HF-ERW / HFI welded)
• Ends: Plain end, bevelled end, or threaded & coupled
• Surface: Black, varnished, galvanized, or coated (FBE / 3LPE / paint)
ERW pipe sizes / ERW pipe size chart (typical ordering reference):ERW pipe sizes / ERW pipe size chart (typical ordering reference):
| NPS | OD (mm) | Sch 40 WT (mm) | Sch 80 WT (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 2.77 | 3.73 |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 2.87 | 3.91 |
| 1 | 33.4 | 3.38 | 4.55 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 3.91 | 5.54 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 5.49 | 7.62 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 6.02 | 8.56 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 7.11 | 10.97 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.18 | 12.70 |
| 10 | 273.0 | 9.27 | 15.09 |
| 12 | 323.8 | 10.31 | 17.48 |
| 14 | 355.6 | 11.13 | 19.05 |
| 16 | 406.4 | 12.70 | 21.44 |
| 18 | 457.0 | 14.27 | 23.83 |
| 20 | 508.0 | 15.09 | 26.19 |
| 24 | 610.0 | 17.48 | 30.96 |
A procurement-ready ERW pipe specification typically states: governing standard and product form (ERW welded pipe / HF-ERW), grade, size expression (NPS/Schedule or OD/WT), length (SRL/DRL/fixed), ends (plain/bevelled/threaded & coupled), surface/coating, weld seam NDT scope, hydrostatic test requirement (when applicable), dimensional tolerance, marking/traceability, and EN 10204 3.1 / 3.2 documentation.
| Standard | Product Type | Typical Grades | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| API 5L | ERW Pipe | Gr.B, X42–X60 (on request) | Onshore ERW pipe for oil, gas and water transportation |
| ASTM A53 | ERW Carbon Steel Pipe | Grade A, Grade B | Water, gas, low-pressure fluid service and mechanical use |
| ASTM A135 | ERW Pipe (Type E) | Grade A, Grade B | Fire mains, sprinkler systems, water and gas distribution |
| EN 10219 | ERW Structural Pipe | S235, S275, S355 | Structural ERW pipe for construction frameworks and supports |
For ASTM A53 ERW pipe, procurement language frequently uses “A53B” to indicate ASTM A53 Grade B, so a53b erw pipe and a53 gr b erw pipe typically describe the same grade/product form when ERW is specified. Many purchase orders also specify the finish (black or galvanized), size expression (NPS/Schedule), and acceptance deliverables under ASTM A53 ERW pipe specifications, including MTC and any additional testing scope required by the project.
On request, ERW pipe can be supplied with restricted chemistry, improved weld-ability, and additional impact testing for low-temperature or specific project requirements.
ERW Pipe(High-Frequency)Manufacturing Process
ERW steel pipe (HF-ERW / HFI welded pipe) is produced from steel coil in a continuous, highly controlled process:
• Uncoiling & Slitting – Hot rolled or pickled coil is uncoiled and slit to precise strip width, matching the required ERW pipe diameter.
• Forming – The strip passes through a series of forming rolls that gradually bend it from flat strip into an open circular section.
• High-Frequency Electric Resistance Welding– In high-frequency ERW, the strip edges are heated by high-frequency current and immediately forged together under squeeze pressure. The result is a straight-seam weld without filler metal, often called electric resistance welded pipe or HFI welded pipe.
• Weld Seam Removal & Heat Treatment– Internal and external weld beads are trimmed as required. For many standards, the weld area is locally normalized / heat treated to refine grain structure and harmonize properties across the weld seam.
• Sizing & Straightening– The welded pipe passes through sizing stands that control outside diameter and wall thickness, followed by straightening to achieve tight tolerances and low ovality.
• Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)– Modern ERW steel pipe lines use online ultrasonic or eddy current testing on the weld seam. Finished pipes are hydro-tested, visually inspected and dimension-ally checked.
• Finishing & Coating– Pipe is cut to ordered lengths, then ends are bevelled, threaded or left plain. ERW carbon steel pipe can be supplied black, varnished, galvanized, or with external coatings such as 3LPE / FBE / paint for buried or submerged service. In an ERW pipe manufacturing process, purchasing risk is typically closed by process-linked acceptance evidence: strip width/edge condition control, controlled welding parameter windows, weld bead removal consistency, local normalization/heat treatment records when required, sizing/straightening records (OD/ovality/straightness), and documented weld seam NDT coverage. This turns the ERW pipe process into auditable deliverables rather than a narrative description.
This controlled high-frequency ERW process delivers consistent wall thickness, uniform OD and repeatable weld quality – key reasons why ERW pipe has become the standard solution in many non-critical and medium-duty pipelines.
Typical Applications of ERW Carbon Steel Pipe
ERW carbon steel pipe is commonly selected for applications where stable dimensions, reliable weld quality, and cost efficiency are required. Typical uses include:
Water and Gas Distribution
Used in municipal water and gas networks, building service pipelines, and fire protection systems such as sprinkler lines, typically supplied to ASTM A53 or ASTM A135 standards. In these systems, A53 ERW pipe is often ordered by NPS/Schedule with black or galvanized finish, and acceptance is typically closed by MTC plus any specified hydrotest/NDT scope.
Low Pressure Fluid Service
Applied in industrial facilities for cooling water, compressed air, low-pressure oil, and other non-hazardous fluids where consistent pipe geometry and good weld-ability are important. For non-hazardous services, ERW welded pipe procurement commonly focuses on dimensional consistency (OD/WT/ovality), end preparation, and traceable documentation rather than over-specifying seamless form when the code permits welded construction.
Onshore Line Pipe Systems
API 5L ERW line pipe is widely used in gathering lines, utility pipelines, and low to medium pressure transmission systems for oil, gas, and water onshore. API 5L ERW pipe purchasing typically aligns to grade and PSL requirements (when specified by the project), with weld seam NDT scope and traceability structured for inspection release.
Structural and Mechanical Applications
EN 10219 ERW structural pipe is commonly used in building frames, supports, towers, handrails, and general mechanical structures where dimensional accuracy and repeatable strength are required. For structural scopes, ordering language frequently prioritizes tolerances, straightness/ovality control, and consistent markings for batch traceability across fabrication lots.
General Engineering and Fabrication
Suitable for fabricated components such as frames, platforms, racks, ladders, and other assemblies where straightness, ease of welding, and consistent sizing simplify fabrication and installation. In fabrication lots, ERW pipe sizes are often standardized within a project to keep fittings and spools dimensionally aligned and to reduce interface mismatch at assembly.
Quality Control and Testing for ERW Welded Pipe
To ensure reliable performance in pipeline and structural applications, Octal Steel works closely with qualified mills that implement robust and well-documented quality control systems for high-frequency ERW welded pipe production.
• Key quality control and testing measures include:
• Verification of steel coil chemistry and mechanical properties in accordance with API, ASTM, and EN standards
• Precise strip slitting and controlled forming processes to minimize weld misalignment and dimensional deviation
• High-frequency electric resistance welding (HF-ERW / HFI) with strictly controlled welding parameters to ensure stable weld seam quality
• Online ultrasonic or eddy current testing applied continuously to the ERW welded pipe seam during production
• Hydrostatic testing on each pipe length when required by the applicable standard or project specification
• Comprehensive visual inspection, dimensional measurement, and verification of end preparation before delivery
For procurement acceptance, the most referenced closure items are: EN 10204 3.1/3.2 MTC with heat/lot traceability, weld seam NDT records (coverage and results), hydrotest records when applicable, dimensional inspection evidence (OD/WT/ovality/length), and consistent marking/packing that ties bundles to the documentation package.
Full EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2 Mill Test Certificates are provided for ERW welded pipe shipments, documenting chemical composition, tensile properties, impact test results (when specified), and NDT records for each heat and production batch, ensuring complete traceability and compliance.
Why Choose Octal Steel for ERW Steel Pipe
Standards-Based ERW Steel Pipe Supply
Octal supplies ERW steel pipe manufactured in accordance with API 5L, ASTM A53, ASTM A135, EN 10219, and project-specific technical requirements. Each ERW steel pipe shipment is supported by complete EN 10204 3.1 / 3.2 mill test certificates, allowing ERW steel pipe quality and compliance to be verified by owners, EPC contractors, and third-party inspectors.
Cost-Effective ERW Steel Pipe Solutions for Line Pipe Projects
Where design codes and service conditions allow, Octal assists clients in applying ERW steel pipe—including API 5L ERW steel pipe and general ERW carbon steel pipe—as a practical alternative to seamless pipe. This approach enables meaningful cost control on large-volume pipeline projects while maintaining the required safety margins and performance of ERW steel pipe in service.
Complete ERW Steel Pipe Supply Packages
In addition to straight-length ERW steel pipe, Octal can supply matching bends, fittings, flanges, coating systems, and full QA documentation under a single ERW steel pipe supply scope. This integrated approach reduces interface risk, simplifies procurement management, and improves overall project execution efficiency. For packaged scopes, ERW pipe fittings are commonly aligned by the same size system and grade, including elbows, tees, reducers, caps, flanges, short spools, and bends—together with coating compatibility and a unified documentation set. This keeps ERW welded pipe, fittings, and related components auditable under one acceptance package.
Export-Oriented Experience with ERW Steel Pipe Projects
Octal has experience supplying ERW steel pipe for international pipeline and infrastructure projects. Packing, marking, and logistics for ERW steel pipe are arranged to suit long-distance export shipment, with seaworthy packing and documentation prepared for projects in the Middle East, Europe, North America, Africa, and Asia.
Engineering Support for ERW Steel Pipe Selection
Technical support is available for ERW steel pipe selection, including standard comparison, wall thickness confirmation, coating system selection, and practical guidance on ERW steel pipe versus seamless pipe based on actual service conditions and project specifications.
FAQ
Q1: How does Octal keep ERW welded pipe acceptance smooth for EPC and third-party inspection?
A1: Octal aligns ERW pipe specification fields (standard/grade/size expression) with weld seam NDT scope, hydro-test requirement when applicable, and EN 10204 3.1/3.2 documentation. Bundles are marked for heat/lot traceability and matched to the documentation set, so inspection release can close without repeated re-submissions.
Q2: What are common ERW pipe sizes, and how is an ERW pipe size chart used in ordering?
A2: ERW pipe sizes are commonly ordered in NPS with schedule (or OD/WT) and length (SRL/DRL/fixed). An ERW pipe size chart is used as a quick index to map NPS to OD and typical schedules so the RFQ can state the exact size expression required by the governing standard.
Q3: What is ASTM A53 Grade B ERW pipe (A53B ERW pipe) and what do ASTM A53 ERW pipe specifications usually include?
A3: ASTM A53 Grade B ERW pipe is often written as A53B ERW pipe or A53 Gr B ERW pipe in purchasing language. ASTM A53 ERW pipe specifications commonly include NPS/Schedule sizing, finish (black or galvanized), end preparation, and acceptance deliverables such as MTC and any required testing scope stated by the project.
Q4: ERW pipe vs seamless—what typically drives selection, and how is ERW pipe pressure rating determined?
A4: ERW pipe vs seamless selection is typically driven by service severity and the inspection scope required by the specification. ERW pipe pressure rating is determined by the governing design code using OD, wall thickness, grade/allowable stress, temperature derating, corrosion allowance, and code factors; it is not a single universal value tied only to “ERW”.