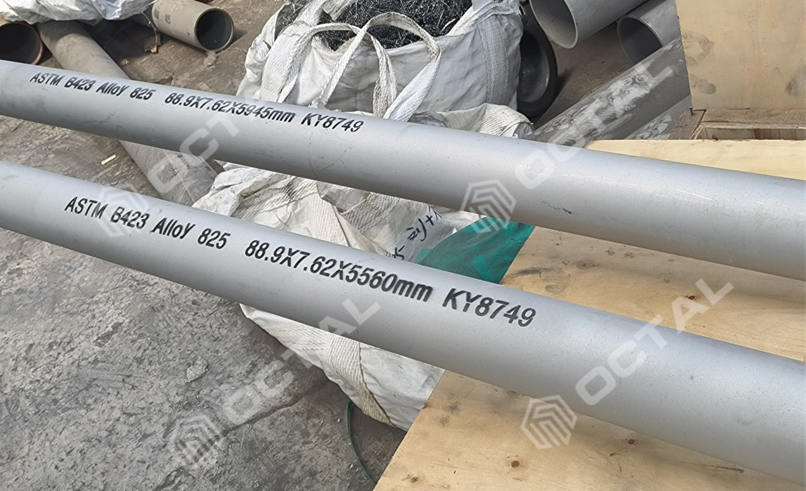
Incoloy 825 / Nickel Alloy 825 / UNS N08825 Pipe and Tube
Inconel 625 (ASTM B444 UNS N06625) Nickel-Chromimum-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloys (Nickel 58%)
Incoloy 825 (ASTM B424 N08825) Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Molybdenum-Copper Alloy (Nickel 38 to 46%)
Wall thickness: SCH 10, SCH 40, SCH STD, SCH 80, SCH XS, SCH 160
Length: 6 meters, 12 meters or customized.
CRA Lined or Clad Pipes with 625 or 825: Lined or clad with carbon steel pipe with mechanical bonding or weld overlay
Incoloy 825 (Nickel Alloy 825 or UNS N08825) is a nickel-iron-chromium alloy with additions of molybdenum, copper and titanium. It is high Nickel content material with minimum Ni 38% to 46%, combined with small value of Mo, Cu and Ti gives Incoly 825 enhanced corrosion resistance to many corrosive environments. It is similar to alloy 800 but has improved resistance to aqueous corrosion. Alloy 825 is especially resistant to sulfuric and phosphoric acids
Incoloy 825 Features
Density 8.14 g/cm3, 0.294 lbs/in3, tensile Strength 586 Mpa (85 Ksi) minimum, yield strength 241 Mpa (35Ksi) minimum, It has excellent resistance to both reducing and oxidizing acids, to stress-corrosion cracking, and to locized attach such as pitting and crevice corrosion.
The higher comprehensive performance of Incoloy 825 is showed in nuclear combustion dissolvers with various corrosive media environment, such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid and sodium hydroxide mixed and processed in the same equipment.
Common Trade Names: Incoloy 825, Alloy 825, Nickelvac 825, Nicrofer 4241, UNS N08825, W.Nr. 2.4858
Applications for Incoloy 825, Nickel Alloy 825, UNS N08825
Due to its superior corrosion resistance characteristics, Incoloy 825 is in use in a number of industries and applications including:
Chemical processing components
Oil and gas piping, recovery
Acid production
Pickling tank heaters, tanks, and equipment
Marine exhaust systems
Pollution control equipment
Calorifiers
Hot vessels for food, water, and seawater
Nuclear fuel reprocessing
Radioactive waste handling
It is an alloy that provides high levels of corrosion resistance to both moderately oxidizing and moderately reducing environments.
Advantages
- Excellent resistance to both reducing and oxidizing acids like sulfuric and phosphoric
- Helps avoid stress-corrosion cracking
- Stops localized attacks such as pitting and crevice corrosion
- High level of resistance to variety of oxidizing substances such as nitric acid, nitrates, and oxidizing salt
Chromium content confers resistance to a variety of oxidizing substances such as nitric acid, nitrates and oxidizing salt.
Molybdenum offers aids resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Titanium addition with an appropriate heat treatment, to stabilize the alloy against sensitization to intergranular corrosion.
Reference Standard material of ALLOY 825
INCOLOY Alloy 825 is designated as UNS N08825 in ASTM AB424 and Werkstoff Number 2.4858. Listed in NACE MR0175 for oil and gas service.
Rod, Bar, Wire and Forging Stock: BS 3076NA16, ASTM B 425, ASTM B 564, ASME SB 425, ASME SB 564, ASME Code Case N-572, DIN 17752, DIN 17753, DIN 17754, VdTÜV 432, ISO 9723, ISO 9724, ISO 9725.
Plate, Sheet and Strip: BS 3072NA16, BS 3073NA16, ASTM B 424, ASTM B 906, ASME SB 424, ASME SB 906, DIN 17750, VdTÜV 432, ISO 6208.
Pipe and Tube: BS 3074NA16, ASTM B 163, ASTM B 423, ASTM B 704, ASTM B 705, ASTM B 751, ASTM B 775, ASTM B 829, ASME SB 163, ASME SB 423, ASME SB 704, ASME SB 705, ASME SB 751, ASME SB 775, ASME SB 829, ASME Code Case 1936, DIN 17751, VdTÜV 432, ISO 6207.
Others: ASTM B 366, ASME SB 366, DIN 17744
Chemical Composition of Incoly 825, Nickel Alloy 825 and UNS N08825
Nickel: 38.00 – 46.00
Chromium: 19.50 – 23.50
Iron: 22.00 min
Titanium: 0.06 – 1.2
Molybdenum: 2.50 – 3.50
Copper: 1.50-3.00
Carbon: 0.05 max
Manganese: 1.0 max
Sulfur: 0.03 max
Silicon: 0.5 max
Aluminum: 0.2 max
Incoloy 825 is available via Continental Steel in wide variety of shapes and forms including, pipe, tube, sheet, strip, plate, round bar, flat bar, forging stock, hexagon, and wire. The various forms of Incoloy 825 meet different critical industrial standards from organizations like ASTM, ASME, BS, SEW, DIN, EN, and ISO.
We stock and supply Incoloy 825, Nickel Alloy 825, UNS N08825 in Pipe, tube, sheet, strip, plate, round bar, flat bar, forging stock, hexagon and wire.
Incoloy 825 Products
Steel Sheet
Steel Plate
Bars
Pipe & Tube (welded & seamless)
Pipe Fittings
Elbows, tees, stub-ends, returns, caps, crosses, reducers, pipe nipples. etc.
Weld Wire (AWS Classification: ERNiFeCr-1 y ENiCrMo-3) Weld overlay 825, Clad 825
Steel Wire
Incoloy 825 VS Inconel 625 (UNS 08825 VS UNS N06625)
In the oil and gas industry, the two most important nickel alloys are Inconel 625 and Incoloy 825. The major difference between two materials is the nickel content value, for Inconel 625 Nickel 58% minimum, and for Incoloy 825 Nickel at range of 38% to 46%. And this makes the 625 material more expensive.
Incoloy 825
lncoloy 825 is an austenitic nickel-iron-chromium-molybdenum-copper alloy also containing high levels of chromium, nickel, copper and molybdenum that can provide high levels of corrosion resistance to both moderately oxidizing and moderately reducing environments.
This balance of alloying elements grants this alloy exceptional resistance to both chloride stress corrosion cracking, as well as crevice corrosion and general corrosion. Chloride stress corrosion cracking is a type of localised intergranular corrosion on materials that are put under tensile strength, in high temperatures and in an environment that includes oxygen and chloride ions such as seawater. The addition of titanium in this alloy also helps to stabilize the alloy against intergranular corrosion.
Like other austenitic, nickel alloy, Alloy 825 is ductile over a wide range of temperatures from cryogenic to well in excess of 1000 °F (538 °C).
Inconel 625
Nickel alloy 625 is nickel-chromium-molybdenum-columbium alloy material, major content Nickel miniumum 58%, also called Inconel 625 or UNS NO6625 under standard ASTM B444 for pipes, or ASTM B443 for plates coils. Other chemical content Chromimum 20% to 23%, Columbium + tantalum 3.15% to 4.15%, Molybdenum 8.0% to 10.0%, columbium Cobalt allow 1.0% max if determined, Iron 5.0% max.
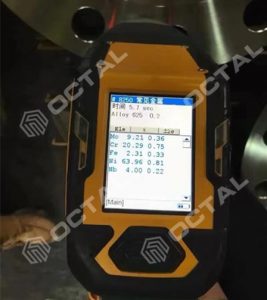
A Solid solution strengthened nickel-based deformed superalloy with molybdenum and niobium as the main strengthening elements. The high strength of Inconel 625 is due to the hardened combination of molybdenum and niobium on the nickel-chromium matrix of the alloy. The addition of molybdenum acts with the niobium to stiffen the alloy matrix, providing a high strength without a strengthening heat treatment.

Inconel 625 is extremely resistant to a variety of unusually severe corrosive environments, including high temperature effects such as oxidation and carburization, including corrosion. Because of the solid solution of the refractory Co and Mo in a Nickel-Chromium matrix, provides 625 an outstanding strength and toughness in high temperature ranging from low up to 2000°F (1093°C).
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF INCOLOY 825
Ultimate Tensile Strength: 85 KSI min (586 MPa min) Yield Strength: (0.2% offset) 35 KSI min (241 MPa min) Elongation: 30% mi
FINISHES
Finish showed with surface smooth grade like other stainless steel products:
- 1 – Hot rolled annealed and descaled. It is available in strip, foil and ribbon. It is used for applications where a smooth decorative finish is not required.
- 2D – Dull finish produced by cold rolling, annealing and descaling. Used for deep drawn parts and those parts that need to retain lubricants in the forming process. #2B – Smooth finish produced by cold rolling, annealing and descaling. A light cold rolling pass is added after anneal with polished rolls giving it a brighter finish than 2D.
- BA- Bright annealed cold rolled and bright annealed
- CBA- Course bright annealed cold rolled matte finish and bright anneal
- 2 – Cold Rolled
- 2BA- Smooth finish produced by cold rolling and bright annealing. A light pass using highly polished rolls produces a glossy finish. A 2BA finish may be used for lightly formed applications where a glossy finish is desired in the formed part. Polished – Various grit finish for specific polish finished requirements. * Not all finishes are available in all alloys – Contact Ulbrich Sales for more information.
HEAT TREATMENT
Heat treatment usually by annealed and tempered. lncoloy Alloy 825 cannot be hardened heat treating.
Our Supply Range For Nickel Alloy 625
Standard and Grades: ASTM B424 N08825/ ASTM B444 UNS N06625
825 Material types: Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Molybdenum-Copper Alloy
625 Material types: Nickel-Chromimum-Molybdenum-Columbium Alloys
Manufacturing types: Seamless hot rolled, anneald; Welded
Sizes: 1/2” to 16”
Wall thickness: SCH10, SCH 20, SCH 40, SCH STD, SCH 80, SCH XS, SCH 160
Length: 6 meters, 12 meters or customized.
CRA Lined or Clad Pipes with 825 or 625: Lined or clad with carbon steel pipe with mechanical bonding or weld overlay



















