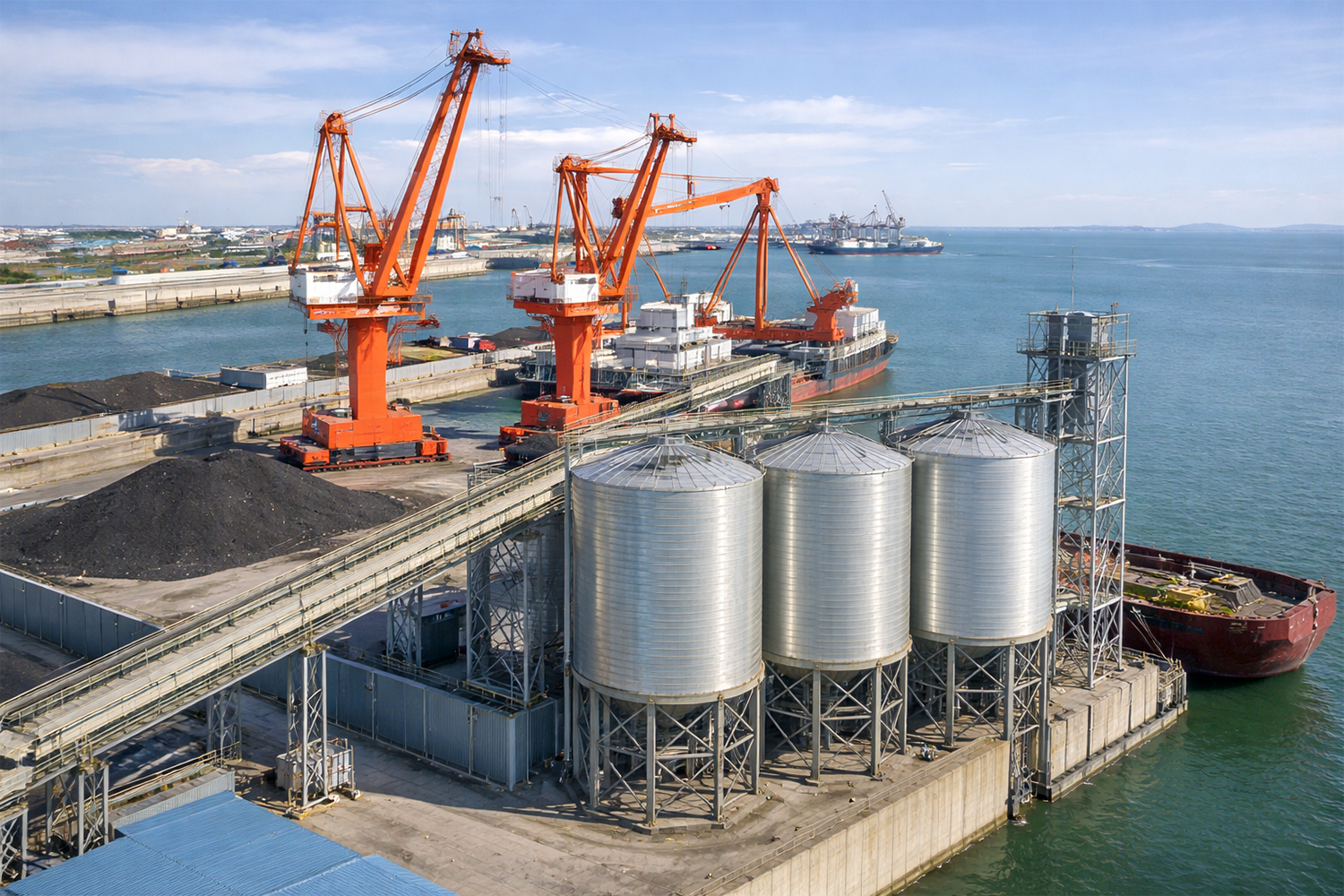
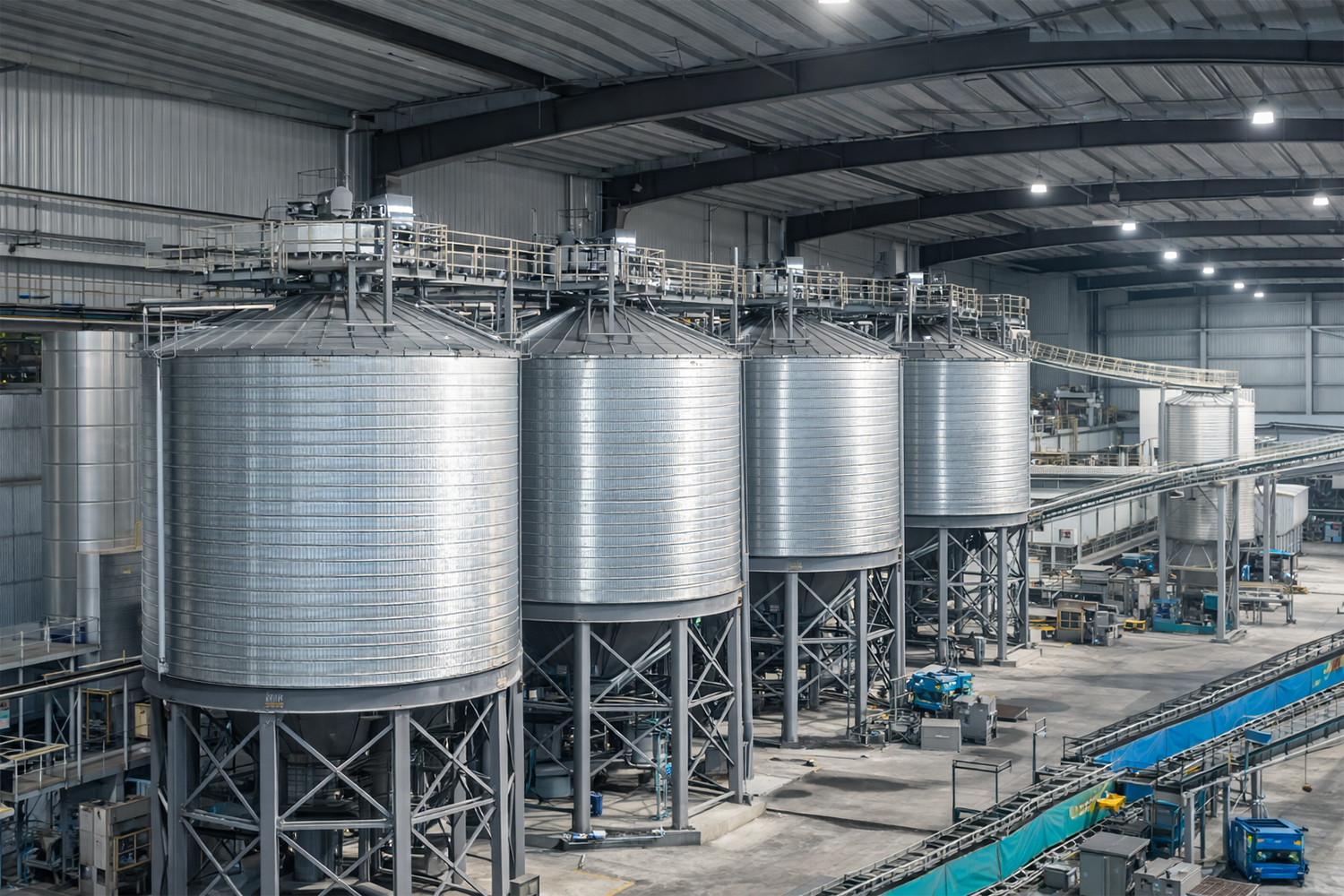
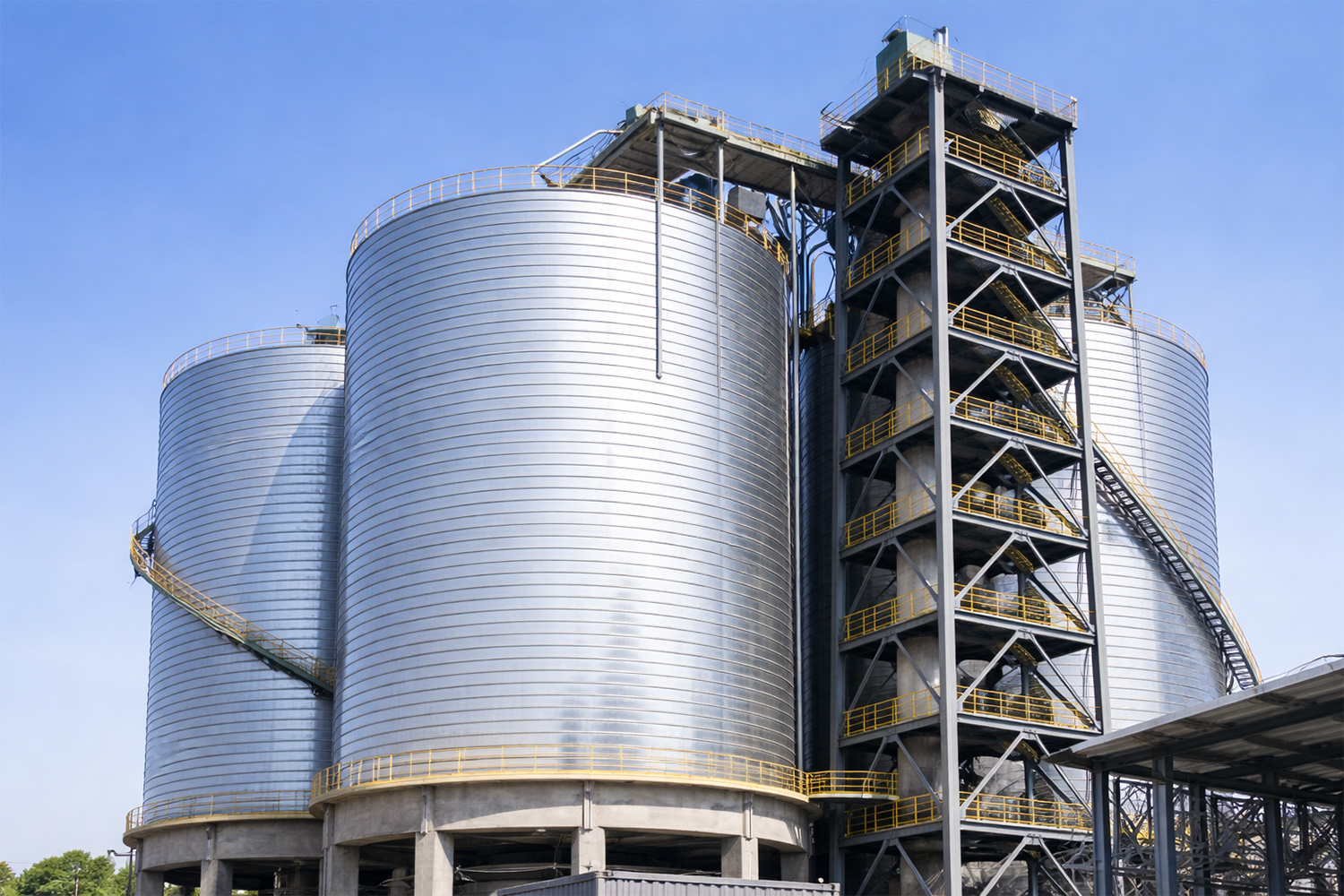
China Steel Silo for Bulk Storage and Handling Systems
China steel silo scope: China steel silos + system solution equipment + related liquid tanks
Range: 100–20,000 m³; Diameter: φ3–35 m
Silo types: spiral, welded, bolt-assembly, insulated, plus material-specific silos (grain/powder/biomass/sulfur/urea/melamine)
System modules: conveying/lifting, dust collection, discharge & pneumatic transfer, valves, ton-bag packaging
10 system scenarios: petroleum coke, battery line, logistics transfer, alumina, PVC, building materials, fly ash, slag powder, grain, mining
Key targets: enclosed dust control (GB13223-2020 for fly ash); automation 40%+ labor saving; slag dust <10 mg/m³ and 70%+ less manual intervention
Supply boundary: structure-only or integrated package (transfer + dust + discharge + packaging)
A China steel silo is a steel storage structure used to hold bulk powders or granules and connect directly to conveying, dust control, metering, and packaging interfaces. China steel silo scope is typically defined by stable storage + controlled discharge + interface readiness for downstream production or logistics. This equipment scope supports materials such as petroleum coke, fly ash, slag powder, mineral powder, grain, biomass pellets/wood chips, PVC granules, alumina, sulfur, urea, and melamine—where China steel silo performance is evaluated at enclosure integrity, discharge stability, and transfer continuity.
This product entry covers three equipment categories under one directory: China steel silo structures, China steel silo system solution modules, and liquid tank utilities.
Product scope overview

Steel silo
This China steel silo category includes structural silo variants selected by material behavior, site constraints, and installation approach.
• Spiral Silo
• Welded Silo
• Bolt Assembly Silo
• Insulated Steel Silo
• Grain Steel Silo
• Mineral Powder Steel Silo
• Biomass Pellet / Wood Chip Steel Silos
• Sulfur Steel Silos / Urea Steel Silos / Melamine Steel Silos
• Steel Silo Roof (China steel silo roof/top options)
Silo system solution
This China steel silo system category groups the modules that make storage “work as a system” from receiving to discharge, transfer, and packaging. China steel silo procurement scopes often close faster when these interfaces are defined as one deliverable boundary.
• Bulk Processing Equipment
• Silo Dust Collector
• Silo Bucket Elevator
• Mining Belt Conveyor
• Air Chute
• Silo Pump
• Inflation Equipment
• Ton Bag Packaging Machine
• Valves for the Building Materials Industry (China steel silo interfaces)
Liquid tank
Related storage tanks are included for projects that combine bulk solids handling with liquid storage utilities.
• Galvanised Steel Storage Tank
• Stainless Steel Storage Tank
• Composite Elevated Storage Tank
• Carbon Steel Storage Tank
For plate grade selection and material grouping under API 650 storage tank scopes, see API 650 Tanks Steel Plates Material Specification.
Capacity range and engineering envelope
Standard engineering coverage for the China steel silo structures and China steel silo system solutions in this entry includes:
Capacity: 100–20,000 m³
Diameter: 3 m–35 m (φ3 m–φ35 m)
Typical specification inputs used to lock the purchase definition and China steel silo interfaces include:
Material name and behavior: bulk density, moisture, flowability, tendency to bridge/rathole, abrasion
Environment: coastal/corrosive atmosphere, temperature swing, rainfall/icing, site wind/seismic basis
Process requirements: throughput, continuous vs batch, buffer time, segregation requirements
Dust and compliance scope: enclosure, dust collection target, emission limits where applicable
Automation scope: level measurement, interlocks, batching/feeding logic, packaging/loading method
Interface equipment list: conveying route, receiving/discharge points, valves, packaging, and dust control boundaries
Silo Structure Options
Different China steel silo structures are selected based on site constraints, construction method, and system integration boundary.
Spiral Silo
A China steel silo spiral configuration is commonly selected where modular forming and efficient site assembly support schedule control and consistent geometry for large capacities.
Welded Silo
A China steel silo welded option is commonly selected where shop fabrication or controlled field welding fits the project’s quality plan, with acceptance anchored on weld procedure/inspection scope and long-term structural integrity.
Bolt Assembly Silo
A China steel silo bolt-assembly route is commonly selected where transport constraints, phased installation, or maintenance access favor segmented delivery, with sealing details and bolt management included in the acceptance package.
Insulated Steel Silo
Commonly selected when condensation control, temperature stability, or material behavior is sensitive to ambient fluctuations, and the insulation interface is part of the delivered scope.
China steel silo option selection matrix (Spiral vs Welded vs Bolt Assembly vs Insulated)
| Silo Option | Typical Selection Drivers | Key Controls in Acceptance | Common System Integrations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spiral Silo | Large capacity coverage Efficient site assembly workflow Consistent geometry for bulk storage |
Marking & lot mapping (if required) Dimensional checks at interfaces Roof/top structure and sealing details |
Dust collector Belt conveyor / bucket elevator Air chute / discharge aids |
| Welded Silo | Fabrication-route preference Quality plan aligned to welding scope Long-term structural integrity focus |
Weld procedure and inspection scope Interface fit-up and tolerance control Coating/finish records (when included) |
Dust collector Bulk processing equipment Valves and metering interfaces |
| Bolt Assembly Silo | Transport constraints Phased installation and maintenance access Segmented delivery boundary |
Bolt control and sealing detail list Packing list mapping for assemblies Interface alignment points for system tie-in |
Bucket elevator / belt conveyor Dust collector Packaging/loading interfaces |
| Insulated Steel Silo | Condensation control boundary Temperature swing management Material stability under ambient changes |
Insulation interface definition Finish protection during transport/storage Interface sealing around nozzles/penetrations |
Dust collector Pneumatic / air chute interfaces Automated feeding/packaging (as ordered) |
Silo system solutions by industry
10 system scenarios matrix
Each scenario below keeps the same China steel silo engineering envelope (100–20,000 m³; φ3–35 m) while adapting to material behavior and process interfaces.
| System Scenario | Capacity Range | Key Control Focus | Typical Equipment Package |
|---|---|---|---|
| Petroleum Coke Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Enclosed dust control Abrasion exposure Stable discharge |
Steel silo Silo dust collector Belt conveyor / bucket elevator Discharge aids + loading/export |
| Lithium Ion Battery Production Line Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Clean transfer Segregation control Stable metering interfaces |
Steel silo Dust collector Controlled conveying Valves + packaging interface |
| Logistics Transfer Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
High throughput transfer Fast loading/unloading Automation-ready flow |
Steel silo Belt conveyor / bucket elevator Air chute Dust control + loading/export |
| Alumina Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Fine powder dust control Flow stability Sealed interfaces |
Alumina steel silos Dust collector Air chute Silo pump / inflation equipment |
| PVC Granule Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Granule integrity Segregation control Automated transfer |
Steel silo Bucket elevator / belt conveyor Valves Ton bag packaging machine |
| Building Materials Industry Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Batching stability Dust removal Continuous feeding |
Steel silo Bulk processing equipment Valves + dust collector Conveying interfaces |
| Thermal Power Plant Fly Ash Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Fully enclosed + dust removal GB13223-2020 target Automation cost reduction 40%+ |
Fly ash steel silo Dust collector Air chute / silo pump Packaging/export interface |
| Steel Plant Slag Powder Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Dust emission <10 mg/m³ Automation manual reduction 70%+ Stable powder export |
Steel silo Dust collector Conveying + discharge aids Packaging/loading |
| Grain Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Stable storage Controlled discharge Transfer compatibility |
Grain steel silo Bucket elevator / belt conveyor Discharge + transfer interfaces |
| Mining Silo System | 100–20,000 m³ φ3–35 m |
Abrasive materials High-duty continuous transfer Dust containment |
Steel silo Mining belt conveyor Silo bucket elevator Dust collector |
Each system below keeps the same engineering envelope (100–20,000 m³; φ3–35 m) while adapting to material behavior and process interfaces.
Petroleum Coke Silo System

Product overview
This petroleum coke silo system automates and stabilizes the full material path—from enclosed storage to accurate batching and controlled conveying—so petroleum coke can be delivered to downstream processes with repeatable ratios, fewer operator touches, and lower dust loss. Designed for petroleum coke storage and controlled discharge where dust containment and abrasion exposure are system-defining factors, the system typically combines a galvanized spiral steel silo, sealed transfer interfaces, and an intelligent batching platform to improve production continuity while reducing human error and unnecessary energy consumption.
Specifications: 100–20,000 m³ (Diameter: 3 m–35 m)
Key control focus: enclosed handling, dust capture, abrasion management, discharge stability. Tight sealing helps prevent moisture ingress, oxidation risks, and dust overflow at storage and transfer points. Discharge stability is commonly protected by conical or flat-bottom configurations with arch-breaking/vibration or fluidizing aids to reduce compaction and bridging. Where petroleum coke is treated as flammable in the project safety plan, typical scope boundaries include ventilation, explosion protection elements, and temperature monitoring to keep storage and discharge safer during continuous operation.
Typical equipment package: steel silo + silo dust collector + conveying (belt conveyor / bucket elevator) + discharge aids + packaging/loading interface.
Spiral Steel Silo Storage Bin
| Structural Features | |
|---|---|
| Material | Made of high-strength galvanized steel plate, rolled by spiral biting process, with excellent compression resistance, moisture resistance, and corrosion resistance. |
| Capacity | Can be designed according to demand (typically 100–20,000 m³); diameter commonly 3–30 m (project-defined), suitable for bulk petroleum coke storage. |
| Advantages | |
| Quick installation | Mechanical automation molding, modular assembly, no welding required, shorter construction period. |
| Good sealing | Helps prevent petroleum coke from moisture exposure, oxidation issues, and dust overflow. |
| Smooth discharge | Conical or flat-bottom design with vibration arch-breaking device or fluidizing device to reduce compaction and bridging. |
| Supporting Equipment | |
| Material level monitoring | Radar/ultrasonic sensors monitor inventory in real time. |
| Dust removal system | Silo-top pulse dust collector to meet environmental protection requirements. |
| Safety facilities | Explosion-proof valve, ventilation opening, temperature monitoring (for flammable petroleum coke scopes as specified). |
Intelligent Batching System
| Core Technology | |
|---|---|
| Automatic metering | High-precision weighing sensors (±0.1%–0.5%) linked with a variable-frequency speed regulating screw feeder to achieve dynamic proportioning. |
| Intelligent Control | |
| PLC/DCS control | Integrated formula management, error compensation, and fault alarm functions. |
| AI algorithm | Optimizes batching parameters through historical data to reduce fluctuations. |
| Multi-component mixing | Supports multi-component proportioning of petroleum coke and additives (e.g., asphalt coke, catalyst materials) as specified. |
| Workflow | |
| Raw material storage | Petroleum coke is stored in the spiral steel silo through conveying equipment. |
| Demand trigger | The system receives production instructions and calls the preset formula. |
| Accurate unloading | The screw feeder draws material by set flow rate and adjusts belt scale / loss-in-weight scale feedback in real time. |
| Mixed transportation | Proportioned material is transferred to the next process (e.g., calcination, molding) as required. |
System Advantages + Application Scenarios
| System Advantages | |
|---|---|
| High efficiency & energy saving | Full automation reduces manual intervention and can reduce energy consumption by 10%–30% (project-dependent). |
| Precise & stable | Dynamic compensation helps control ratio error to ≤0.5% under defined operating conditions. |
| Flexible expansion | Supports IoT integration for remote monitoring and data analysis. |
| Environmental protection & safety | Closed design + intelligent dust removal aligned to PM2.5 and VOCs control expectations, with safety elements defined by project requirements. |
| Application Scenarios | |
| Carbon industry | Petroleum coke and asphalt coke batching for anode and electrode production. |
| Energy field | Blend ratio control for fuel-grade petroleum coke. |
| Metallurgy & chemical industry | Precise feeding where petroleum coke is used as a reducing agent or process raw material. |
Packages can also be released with real-time level monitoring (radar/ultrasonic), an intelligent batching and weighing system (high-precision weighing sensors commonly ±0.1%–0.5% linked with VFD screw feeding), and PLC/DCS logic for recipe management, error compensation, and alarms—supporting multi-component proportioning where petroleum coke is blended with additives such as asphalt coke or catalyst materials. System advantages commonly targeted in project scopes include 10%–30% energy reduction through automation, ratio error control to ≤0.5% via dynamic compensation, IoT-ready remote monitoring, and closed conveying with dust removal aligned to PM2.5/VOC control expectations.
Lithium Ion Battery Production Line Silo System

Product overview
Scope & Control Points
This system is used for automated storage, metering, conveying, and batching of battery powders such as graphite and related additive blends.
Material & structure options
304/316 stainless steel or galvanized steel plate, with spiral-bite forming and high sealing to limit dust escape and reduce moisture pickup.
Batching performance basis
Dynamic weighing + loss-in-weight control; ratio error targets such as ≤0.2% (scope-defined) and typical feeder/weighing accuracy around ±0.1% (system targets often stated ±0.1%–0.5%).
Acceptance boundary (typical)
Negative-pressure enclosed dust removal (e.g., <1 mg/m³ where specified), humidity control (e.g., RH <30%), and PLC/SCADA with MES/ERP traceability (batch logs, alarms, recipe management).
| Item | Typical Specification | What It Controls for Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Functional positioning | Automated storage, metering, conveying, and batching for negative electrode materials (graphite, coke blends, silicon-based powders) | Stable recipe execution and controlled transfer to downstream processes |
| Capacity & size envelope | 100–20,000 m³; diameter φ3–35 m (customized by scope) | Matches buffer time, throughput, and site constraints without rework |
| Silo material options | 304/316 stainless steel or galvanized steel plate (project-defined) | Corrosion/cleanliness alignment to powder sensitivity and plant requirements |
| Forming & sealing route | Spiral-bite process; high sealing, typically configured to reduce oxidation/moisture absorption | Lower dust leakage and reduced moisture-driven quality drift |
| Bottom & discharge design | Conical gravity flow + vibration/pneumatic arch breaking; flat-bottom with mechanical scraper (material-dependent) | Controls bridging/agglomeration and stabilizes feed to batching equipment |
| Batching accuracy targets | Dynamic weighing + intelligent control; ratio error targets such as ≤0.2% (scope-defined); feeder/weighing accuracy often ±0.1% (system performance commonly stated ±0.1%–0.5%) | Defines whether the recipe can be released without repeated tuning onsite |
| Metering & feeding hardware | Sealed double screw feeder (dustproof) + loss-in-weight scale; vibrating feeder option for granular graphite | Consistency of make-up rate and reduced powder escape at interfaces |
| Conveying route | Pneumatic conveying (low breakage for powders) and/or closed screw conveyor (dust-proof, leak-proof) | Clean transfer and stable material delivery to mixers/next step |
| Dust control | Pulse bag dust removal + negative-pressure suction at roof; targets such as dust concentration <1 mg/m³ where specified | Cleanroom-aligned dust containment and compliance closure |
| Moisture & environment control | Heating/dehumidification options; targets such as RH <30% for hygroscopic powders | Reduces moisture pickup, oxidation risk, and batch variability |
| Controls & data | PLC/SCADA with recipe management, error compensation, alarms; MES/ERP integration for traceability; batch/ratio/time records upload | Traceable batches and faster QA release (evidence-based acceptance) |
| Safety protection | Explosion-proof valves; CO₂/N₂ inerting options (for flammable powders); temperature/humidity monitoring | Risk controls tied to EHS review and commissioning readiness |
Logistics Transfer Silo System

Applicable to seaports, railway hubs, and large-scale building materials logistics parks.
Scope & Control Points
Built for high-turnover cement and building-material transfer at seaports, railway hubs, and bulk logistics parks—where the purchase definition is driven by fast transit storage, sealed dust control, and automation-ready dispatch.
Engineering envelope (typical)
Capacity: 100–20,000 m³; Diameter: φ3–35 m (site-dependent)
Throughput & dispatch basis
Acceptance is commonly anchored on loading/unloading rate, truck/ton-bag/bulk interface definition, and stable transfer without congestion at peak shipping windows.
Dust & enclosure basis
Fully enclosed storage + closed conveying corridor, with dust collection performance defined at transfer points to control fugitive dust during unloading/loading.
Automation & data integration
Inventory visibility (level/weight), order-based allocation, and dispatch traceability—typically reviewed via PLC/IoT readiness and ERP/MES connectivity where required.
Typical equipment package
Steel silo + belt conveyor/bucket elevator + air chute/discharge aids + silo dust collector + loading/packaging interface (as ordered)
| Procurement Scope | Typical Range / Basis | Key Control Points in Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Applicable Scenarios | Port terminals (bulk transshipment) Rail logistics bases (container/bulk unloading) Regional cement distribution centers Large-scale building materials logistics parks |
High turnover with predictable dispatch Order-based inventory allocation Closed transfer route to reduce dust escape |
| Silo Structure | Capacity: 100–20,000 m³ Diameter: φ3–35 m Height: ≤30 m (typical; customizable) Material: galvanized steel plate / carbon steel + anti-corrosion coating Forming: spiral-bite, no welding (where specified) |
Corrosion/environment suitability (coastal salt spray if applicable) Sealing at roof, manholes, nozzles, and discharge Bottom discharge configuration aligned to logistics mode Wind/seismic basis confirmation (docks/railway sites) |
| Loading / Unloading | Ship/train unloading: pneumatic pump or screw ship unloader Typical unloading rate: 200–800 t/h Truck loading: automatic loader Weighing accuracy: ±0.5% (typical) |
Throughput verification at receiving/loading points Weighing and loading repeatability Interface fit-up to trucks/ton bags/bulk tankers |
| Dust & Environmental Control | Fully enclosed structure + closed conveying corridor Silo-top dust collector (pulse bag / cyclone as ordered) Dust emission target: ≤20 mg/m³ (where specified) |
Enclosure integrity (leak-proof transfer) Dust collector sizing and performance evidence Compliance boundary aligned to local PM control requirements |
| Monitoring & Automation | Level monitoring: radar/level + weight sensors Temperature/humidity sensors (anti-caking control) PLC + IoT (as ordered) ERP/MES connectivity (inventory + shipping records) |
Real-time inventory visibility for dispatch Order-driven allocation logic and shipment traceability Alarm list, data logs, and system handover documents |
| Typical Equipment Package | Steel silo Belt conveyor / bucket elevator Air chute / discharge transfer aids Silo-top dust collector Truck/ton-bag loading interface (as ordered) |
Single boundary definition (structure + transfer + dust + loading) Interface list matches site tie-in points Commissioning checklist aligned to logistics workflow |
Alumina Silo System

Applicable scope
Built for large-scale alumina powder (Al₂O₃) storage and transfer where fine-powder behavior drives the purchase definition—sealed dust control, stable discharge, and wear-managed conveying interfaces.
Engineering envelope (typical)
Product specifications: 100–20,000 m³; Diameter: φ3–φ35 m (site- and duty-dependent)
Scope & control points
Acceptance is typically anchored on fully enclosed handling, dust/emission limits at transfer points, bridging/ratholing prevention, wear protection on conveying/valves, anti-static / explosion-risk controls (when specified), and transfer continuity to downstream process or truck/ton-bag export.
| Item | Specification / Acceptance Focus |
|---|---|
| Duty boundary | Storage + controlled discharge + transfer continuity (receiving / in-plant conveying / export loading) |
| Capacity & diameter | 100–20,000 m³; φ3–φ35 m (site- and duty-dependent) |
| Enclosure & dust | Fully enclosed handling + dust collection defined at charging/discharge transfer points (emission limits where specified) |
| Discharge stability | Flow aids basis (fluidization / vibration) to prevent bridging and maintain stable discharge |
| Wear & service life | Wear-managed conveying/valve interfaces for abrasive alumina; maintenance boundary clarified in scope |
| Moisture & agglomeration | Sealing + optional dehumidification / nitrogen protection interfaces (scope-defined) |
| Safety (when required) | Grounding/anti-static + explosion vent + inert gas protection (N₂/CO₂) + O₂ monitoring (as specified) |
| Control & data | Inventory/alarms/remote visibility; optional MES upload boundary where required |
| Category | Focus | Typical controls / package |
|---|---|---|
| Powder behavior | Fine particles / dust | Fully enclosed structure + roof dust collector; transfer-point dust capture defined where specified |
| Powder behavior | Moisture pickup / agglomeration | Sealed interfaces; humidity monitoring; dehumidification or nitrogen filling interface (scope-defined) |
| Powder behavior | Abrasion (high hardness) | Wear-resistant conveying/valve interfaces; optional inner-wall wear coating (scope-defined) |
| Powder behavior | Static electricity risk | Grounding + anti-static filtration; explosion vent + inerting (N₂/CO₂) where required |
| Equipment package | Alumina steel silo | Galvanized steel sheet or 316L stainless steel; sealed flanges/nozzles; anti-static provisions (as specified) |
| Equipment package | Dust collection | Pulse-bag dust collector on silo roof; filtration/emission targets where specified |
| Equipment package | Feeding / charging | Pneumatic conveying (dilute phase) or closed screw conveyor (scope-defined) |
| Equipment package | Discharge | Rotary valve + pneumatic transfer to process, or truck/ton-bag loading boundary |
| Equipment package | Flow aids | Bottom air-fluidization plate and/or vibration arch breaking to prevent bridging |
| Equipment package | Instrumentation | Temperature/humidity sensors; O₂ monitoring and nitrogen interface (when required) |
| Equipment package | Metering / control | Loss-in-weight scale or nuclear scale (scope-defined) + screw feeder for stable flow control |
| Equipment package | Remote / IIoT (optional) | Inventory & alarms visibility; mobile/PC viewing; data upload boundary where required |
PVC Granule Silo System

Product overview — PVC Granule Silo System (Scope + Control Points)
Built for PVC granule storage and controlled transfer where the purchase definition is driven by granule integrity + low-dust handling + segregation/traceability + stable feeding. It is commonly applied as an upgrade from open-air stacking or ordinary silos to reduce moisture pickup, static accumulation, dust generation, and discharge bridging, while improving inventory control and automated material dispatch.
Engineering envelope (typical)
Capacity 100–20,000 m³; Diameter φ3–35 m (site- and process-dependent).
Procurement control points (typical)
⒈Material & lining: galvanized steel or carbon steel with PE/PP anti-static lining options for contamination and static control.
⒉Thermal & moisture stability: ventilation/heat protection for temperature sensitivity (softening/agglomeration risk), plus RH monitoring targets (e.g., RH <40% where specified).
⒊Static & dust: grounding + conductive measures; enclosed conveying with dust collection at transfer points (e.g., emission <10 mg/m³ where specified).
⒋Discharge reliability: conical bottom + vibration/fluidizing/arch-breaking to keep flow stable; rotary valve + VFD screw conveying for controlled discharge.
⒌Segregation & traceability: RFID/scan identification for different PVC grades (e.g., SG-5/SG-8), with batch records and optional MES connectivity.
⒍Metering basis: loss-in-weight/flow metering with accuracy targets (e.g., ±0.5% scope-defined).
| Procurement Item | PVC Granule Risk / Why It Matters | Typical Design / Acceptance Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Scope boundary | Storage + sealed transfer + controlled discharge for PVC granules used in downstream extrusion/injection or blending lines | Structure-only or integrated package covering transfer, dust control, discharge and packaging interfaces (as ordered) |
| Engineering envelope | Project-dependent capacity/diameter selection affects buffering time, loading rate and interface sizing | Capacity: 100–20,000 m³ Diameter: φ3–35 m |
| Granule behavior controls | 2–5 mm granules flow well but can adsorb under static; heat >60°C may soften/agglomerate; some grades absorb moisture; transfer can generate fines/dust |
Ventilation / heat protection at the top zone; sealed handling to limit dust escape; moisture control defined by scope (e.g., RH monitoring) |
| Structure & material options | Contamination risk and static build-up drive material and lining choices | Galvanized steel or carbon steel with PE/PP lining (anti-static/corrosion-resistant) as specified |
| Discharge stability | Bridging and unstable discharge cause feed fluctuation and grade mixing | Conical bottom + vibration motor or fluidizing/arch-breaking device; rotary valve + VFD screw conveying for controlled discharge |
| Static & dust compliance | Electrostatic accumulation and dust leakage impact safety and housekeeping; fines can increase during conveying | Grounding + conductive measures; silo-top cartridge/pulse dust collector (e.g., emission <10 mg/m³ where specified); optional nitrogen protection for dusty environments |
| Segregation & grade ID | Mixing grades (e.g., SG-5/SG-8) or losing identity creates NCRs and rework in production | RFID tags / scanning to distinguish grades; inventory records aligned to dispatch and packaging interfaces |
| Metering & data traceability | Stable feeding improves downstream blending/extrusion consistency; batch logs support QA closure | Loss-in-weight scale or flow meter (e.g., accuracy ±0.5% scope-defined); batch/usage data upload with optional MES connectivity |
| Typical equipment package | Interfaces define procurement completeness (transfer + valves + packaging) | Steel silo + bucket elevator / belt conveyor + valves + packaging interface (ton bag packaging machine where used) |
Building Materials Industry Silo System

Product overview
Scope & Control Points
This system supports bulk storage and multi-silo batching for cement, clinker, mineral powder, fly ash/gypsum and related building materials—where the purchase definition is driven by stable ratio control, enclosed dust compliance, and continuous feed to downstream processing and dispatch.
Engineering envelope (typical)
Capacity: 100–20,000 m³; Diameter: φ3–φ35 m (site- and material-dependent)
Acceptance boundary (typical)
Batching stability (multi-bin coordination), dust removal performance at transfer points, continuous feeding without congestion, and automation/data readiness for scheduling and traceable dispatch.
Typical equipment package
Steel silo + bulk processing equipment + conveying interfaces + dust collector + discharge/feeding + valves and metering interfaces (as ordered)
| Module / Area | Technical Points (Typical) | Procurement Acceptance Checks | Value in Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage structure | Spiral interlocking galvanized steel plate (typ. 2–6 mm where specified) Cone-bottom design (typ. ≥60°) + arch-breaking / fluidization option Multi-silo cluster layout for coordinated batching |
Capacity/diameter confirmation (100–20,000 m³; φ3–φ35 m) Interface dimensions for discharge & conveying tie-ins Residual/unloading basis (e.g., low-residue target where specified) |
Higher storage density vs open yards Faster project deployment vs concrete rounds (route-dependent) Better feed continuity under peak shipping windows |
| Dust control & enclosure | Pulse-bag dust removal + pressure-difference self-cleaning (where specified) Dust capture defined at transfer points and loading/unloading nodes Enclosed storage + closed conveying corridor concept |
Dust emission limit basis (e.g., <20 mg/m³ or project PM/standard target) Negative pressure / sealing points list Filter/collector model & maintenance access definition |
Reduced fugitive dust during dispatch Easier environmental compliance closure at site acceptance |
| Batching & discharge | Frequency-controlled screw feeder / controlled discharge Metering by scale/flow measurement (e.g., ±0.5% basis where specified) Multi-bin coordinated batching for mineral powder/fly ash/gypsum mixes |
Ratio error target basis (e.g., dynamic ratio error <0.8% where specified) Throughput window confirmation (t/h) + stable feeding proof points Discharge mode: bulk truck / ton bag / process feed interface |
More stable batching = fewer downstream quality swings Higher dispatch efficiency with less manual intervention |
| Monitoring & scheduling | Level radar (e.g., ±0.1 m where specified) + temperature sensor (anti-condensation warning) Intelligent allocation by order / inventory logic ERP connectivity for delivery planning; truck reservation logic (where required) |
Signal list & IO definition (level/weight/temperature) Scheduling logic boundary (order allocation, dispatch traceability) Integration readiness (ERP/MES/dispatch records) as required |
Faster turnaround with fewer queue bottlenecks (site-dependent) Cleaner accountability via inventory + shipping records |
| Typical scope bundle | Steel silo(s) + dust collector + conveying interfaces Bulk processing / discharge aids + metering/feeding Valves and building-material industry interfaces |
BOM boundary (structure-only vs integrated package) Packing list mapping & equipment ID marking (where specified) Commissioning interface checklist |
One boundary for EPC review and site acceptance closure Reduced rework caused by missing interface definition |
Thermal Power Plant Fly Ash Silo System

Product overview
Built for fully enclosed storage + metered export of thermal-power by-products—fly ash, desulfurization lime powder, and FGD gypsum—where environmental compliance and export efficiency are tied to plant operating cost and by-product value recovery. Typical projects specify dust-control performance aligned to [GB13223-2020], and use automation to cut manual intervention and stabilize truck/ton-bag dispatch.
Product specifications (typical)
Capacity 100–20,000 m³; Diameter φ3–φ35 m (site-dependent).
Scope & control points
• Dust compliance: fully enclosed storage + sealed transfer, with pulse-bag dust removal at key transfer points to control fugitive dust during loading/unloading.
• Material-driven safety: fly ash may contain unburned carbon; monitoring and protection are configured to reduce spontaneous-combustion / dust-explosion risk (e.g., CO monitoring + venting/inerting where specified).
• Moisture & caking control: lime powder is hygroscopic and corrosive; gypsum can stick/harden—design is typically anchored on moisture prevention, anti-caking discharge, and stable pneumatic transfer.
• Export efficiency & automation: unattended loading/dispatch logic, inventory visibility, and ERP updates reduce queue time and improve shipment accuracy; value-added targets are often written as improved by-product export efficiency (e.g., gypsum utilization 60% → 90%) with labor cost reduction 40%+ (scope-defined).
Typical equipment package
Fly ash steel silo + silo dust collector + air chute / silo pump + discharge/arch-breaking aids + ton-bag packaging machine or bulk export/loading interface (as ordered).
Materials, Risks, and Design Responses
| Material | Key Characteristics | Storage / Transfer Risks | Typical Design Controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | Fineness 0.5–200 μm Good fluidity May contain unburned carbon |
High dusting / fugitive dust Explosion / oxidation risk (scope-defined) |
Fully enclosed silo + sealed transfer points Pulse-bag dust removal at transfer points CO monitoring + explosion vent / inerting (where specified) Anti-caking discharge aids |
| Lime powder (FGD) | Highly hygroscopic Strong alkalinity (pH > 12) |
Hardening / clumping Corrosion exposure to containers & interfaces |
Moisture-prevention configuration (humidity sensing, sealing) Corrosion-resistant container / interface selection Stable pneumatic conveying design |
| Desulfurization gypsum (FGD) | Moisture content 10%–15% High viscosity May harden after stacking |
Sticking / bridging Caking during long storage Turnover bottlenecks |
High-angle cone + vibrator/arch-breaking aids Anti-stick lining (e.g., UHMWPE where specified) Fast-turnover export design (scope-defined) |
Procurement Acceptance Boundary
| Acceptance Item | Typical Basis (scope-defined) | Delivered Scope Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental compliance | Fully enclosed + dust removal aligned to [GB13223-2020] | Enclosed silo body, sealed transfer points, dust collector interface list |
| Dust removal performance | Pulse-bag dust collection defined at loading/unloading and transfer nodes | Silo-top/transfer-point dust collector, ducting, negative-pressure sealing (where specified) |
| Safety monitoring | Material level radar (±0.2 m), CO monitoring for fly ash (where specified), humidity sensing for lime powder | Radar level system, CO sensor, humidity sensor, alarm logic |
| Discharge & transfer stability | Anti-caking discharge + stable pneumatic transfer to export/packaging | Air chute / silo pump, rotary valve, fluidization/arch-breaking aids |
| Automated export & data integration | Unattended loading (truck identification), loading error ±0.3% (where specified), ERP real-time inventory/order update | Automatic loading station, weighing/ID, ERP connectivity, inventory & dispatch records |
| Performance targets (project goals) | Automation labor savings 40%+; by-product export efficiency improvement (e.g., gypsum utilization 60% → 90%) | Control strategy + equipment boundary defined per material and export route |
Steel Plant Slag Powder Silo System

Product overview
Configured for steel-plant slag powder handling where dust compliance, abrasion duty, and automated export are tied directly to plant O&M and by-product value capture. It is typically specified for blast-furnace slag (water-quenched / dry) and converter slag streams where moisture variation, high hardness/abrasion, and fine dust drive silo structure, lining, and discharge design.
Product specifications: 100–20,000 m³ (φ3 m–φ35 m)
Key control focus: dust emission control, wear/anti-arching discharge stability, moisture/metal management, packaging & loading continuity, automation & traceability.
Typical equipment package: steel silo + silo dust collector + conveying + air chute / pump interfaces + packaging/loading interface (as ordered).
| Procurement definition | Scope & acceptance boundary (typical) |
|---|---|
| Applicable materials | Blast furnace water-quenched slag (moist, prone to compaction), blast furnace dry slag (hard, abrasive, dusty), converter slag (may contain metallic iron; weathering/expansion behavior). |
| Engineering envelope | Capacity 100–20,000 m³; Diameter φ3–φ35 m (site-dependent). |
| Environmental compliance | Fully enclosed storage + sealed transfer points; dust collector performance commonly defined as dust emission targets such as <10 mg/m³ at specified points. |
| Abrasion & lining duty | Wear-resistant reinforcement for hard/abrasive slag service; cone/bottom anti-wear measures (e.g., anti-wear plate/liner specified by scope). |
| Discharge stability (anti-arching) | Anti-arching package defined by material behavior (e.g., pneumatic fluidization device, vibration/hydraulic arch breaking); residual-rate targets can be specified (e.g., <0.5% for water-quenched slag service where required). |
| Moisture & metal management | Optional inline monitoring for moisture (wet slag) and metal/iron particle detection (converter slag); magnetic separation interface where slag value recovery is part of the scope (e.g., recovery rate targets such as ≥95% can be specified). |
| Automation & batching accuracy | Unattended operation targets defined by plant workflow; automatic batching can be included with error targets (e.g., ≤1% where specified) and interlocks/alarms by PLC/SCADA. |
| Export / packaging interface | Export mode defined per project: bulk loading, ton-bag, or downstream pneumatic transfer; interface sealing and continuity at peak shipping windows included in acceptance review. |
| Typical equipment package | Steel silo + silo dust collector + conveying (belt/screw/pneumatic by scope) + air chute / pump interfaces + valves + packaging/loading interface. |
Grain Silo System

Product overview
Scope & Control Points
This grain silo system is specified for wheat/corn/rice and similar bulk grains where airtight preservation, pest control, and data-driven condition management are part of the procurement acceptance boundary—not only capacity. It is typically selected to reduce mildew/insect loss and keep intake/outfeed stable with mechanized handling and closed storage.
Engineering envelope (typical)
Product specifications: 100–20,000 m³ (φ3 m–φ35 m) (site-dependent configuration)
Preservation basis (what usually gets checked)
Airtight sealing and fumigation capability are commonly defined by airtightness ≤ 500 Pa and pressure half-life ≥ 5 min, with sealed interfaces that support fumigation/insecticide control (e.g., phosphine concentration ≥ 200 ppm where specified).
Temperature & quality stability
Ventilation + circulation control is commonly reviewed to limit internal temperature stratification (e.g., temperature difference ≤ 2°C), supported by distributed sensing (e.g., 1 temperature/humidity point per 100 m²) and early warning signals such as CO₂ monitoring for mold risk.
Discharge & handling continuity
Discharge stability is commonly anchored on cone bottom angle ≥ 45° plus a vibrating discharge device, with low residue targets (e.g., residue < 0.1%) to support turnover without repeated manual clean-out.
Typical equipment package
Grain steel silo + sealing system + ventilation/fumigation interfaces + monitoring (T/RH/CO₂) + discharge aids + conveying interfaces (bucket elevator / belt conveyor) + sampling/automation options (as ordered).
Key parameters procurement teams typically anchor on (table)
| Purchase definition item | What it controls in operation | Typical target / spec language | Typical acceptance checks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airtightness & sealing | Fumigation effectiveness, pest control, moisture ingress | Airtightness ≤ 500 Pa Pressure half-life ≥ 5 min Fumigation concentration holding (e.g., phosphine ≥ 200 ppm where specified) |
Airtightness/pressure test records Sealing design at roof/doors/penetrations Fumigation interface completeness |
| Temperature & ventilation control | Mold inhibition, quality stability, loss reduction | Ventilation + circulation control Internal temperature difference ≤ 2°C (where specified) |
Fan/duct layout & sizing basis Control logic (auto start/stop where used) Trend/report functions |
| Condition monitoring coverage | Early warning + traceable storage conditions | Distributed T/RH sensing (e.g., 1 point per 100 m²) CO2 monitoring for mold risk warning |
Sensor list + layout drawing Alarm thresholds & escalation rules Data export / historian interface Calibration/commissioning records |
| Discharge stability / anti-arching | Turnover efficiency, reduced breakage, less manual intervention | Cone bottom angle ≥ 45° Vibrating discharge device Residue < 0.1% (where specified) |
Bridging/arching mitigation design review Commissioning discharge test (typical grains) Residue/clean-out verification (scope-defined) |
| Pest management readiness | Prevent infestation loss | Airtight + fumigation/insecticide interfaces Optional pest activity recognition (where used) |
Interface list (ports/valves/safety devices) Optional sensor/function acceptance (if ordered) Operating boundary definition (scope split) |
| Automation & sampling options | Reduce labor dependence; support QA | Auto ventilation (weather-linked) where used AGV/auto sampling where specified |
I/O list & control cabinet spec Integration points & protocols Sampling workflow definition FAT/SAT checklist items |
| Value targets (project KPI) | Business justification / performance expectation | Storage loss ≤ 0.5% (often benchmarked vs 1.5%–3%) Total storage cost reduction 25%–40% Modular deployment within 72 h (if modular scope applies) |
KPI assumptions clarified in scope Responsibility split (supplier/site) defined Measurable test/verification method agreed |
Mining Silo System

Product overview
Applied to mining bulk materials and mineral powders where abrasion, high-duty transfer, and sealed dust control define the purchase scope—especially for continuous loading, short dispatch windows, and strict housekeeping requirements.
Product specifications (typical)
Capacity: 100–20,000 m³ · Diameter: φ3–φ35 m
Key control focus
-
Dust containment & compliance: fully enclosed structure with sealed feed/discharge points; roof bag dust collection + negative-pressure exhaust (capture targets commonly stated up to 99%, emission ≤15 mg/m³ where specified).
-
Abrasion exposure & uptime: wear-resistant silo wall / liners and multi-stage arch-breaking to keep discharge stable under harsh material behavior.
-
Moisture stability & stock quality: enclosed storage reduces weather impact; moisture fluctuation targets can be defined (e.g., ±0.5% where specified).
-
Digital inventory & loss control: 3D level measurement + algorithm logic to keep inventory deviation <0.5% and trigger abnormal-loss alarms.
-
O&M readiness: real-time stress/deformation monitoring (warning accuracy ±2 mm), remote control, and mobile visualization.
-
Closed-loop site management: sealed drainage + sedimentation recycling for dust suppression to support “zero discharge” site objectives where required.
Typical equipment package
Steel silo + sealed feed/discharge + belt conveyor / bucket elevator + bag dust collector + negative-pressure exhaust + discharge aids (anti-arching) + level/condition monitoring + loading/packaging interface (as ordered).
Scope & Control Points (Mining Bulk Storage & Transfer)
| Item | Purchase Control Point |
|---|---|
| Applicable scope | Mining bulk materials & mineral powders where abrasion, continuous handling, and enclosed dust control drive the system definition. |
| Product specifications (typical) | Capacity: 100–20,000 m³ Diameter: φ3 m–φ35 m |
| Dust containment | Fully enclosed structure + sealed feed/discharge points + roof bag dust collector + negative pressure exhaust (capture targets may be stated up to 99%; emission limits e.g. ≤15 mg/m³ where specified). |
| Abrasion & high-duty transfer | Wear-resistant silo wall/liners + heavy-duty transfer interfaces sized for abrasive service and continuous operation. |
| Discharge stability | Multi-stage anti-arching / discharge aids to keep flow stable and reduce residue under variable moisture and bulk density. |
| O&M readiness | Real-time stress/deformation monitoring (warning accuracy ±2 mm where specified) + remote control + mobile visualization. |
| Typical equipment package | Steel silo + mining belt conveyor + bucket elevator + dust collector + discharge aids + monitoring + loading/packaging interface (as ordered) |
KPI Comparison — Open-air Storage Yard vs Intelligent Spiral Silo
| Performance Indicators | Open-air storage yard | Intelligent spiral silo | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land utilization rate | 1 ton/m² | 8 tons/m² | 700% |
| Loading efficiency | 150 tons/hour | 800 tons/hour | 433% |
| Moisture content fluctuation | ±3% | ±0.5% | Stability ×6 |
| Environmental compliance | Watering required | Zero-emission design | Fully qualified (as specified) |
Equipment modules inside a typical silo system solution
System packages commonly combine modules across receiving, transfer, discharge, and packaging boundaries.
• Conveying and lifting: mining belt conveyor, silo bucket elevator
• Discharge and pneumatic support: air chute, silo pump, inflation equipment
• Dust and environmental control: silo dust collector
• Processing interfaces: bulk processing equipment
• Control and sealing interfaces: valves for the building materials industry
• Packaging/export interfaces: ton bag packaging machine, loading/export interface as ordered
Materials and corrosion protection option
This entry supports scope language that may include stainless steel silo and galvanized steel silo alongside standard steel silo structures, depending on environment and project definition.
• Steel silo: used broadly across powder and granule storage where structural design, discharge control, and system integration define performance.
• Stainless steel silo: commonly written where corrosion resistance, cleanliness, or specific process requirements are part of the acceptance boundary.
• Galvanized steel silo: commonly written where atmospheric corrosion control is prioritized and long-term exterior protection is part of the deliverable.
• Insulated steel silo: selected where temperature swing, condensation control, or material stability drives insulation requirements.
Quality, compliance, and acceptance package
A release-ready supply package typically aligns structure, interfaces, and documentation so receiving and installation can close without repeated clarification cycles. Acceptance deliverables commonly include:
⒈ Identification and marking aligned to packing lists
⒉ Inspection and dimensional records per purchase definition
⒊ Coating/finish records where included
⒋ System interface list for conveying, dust control, discharge, and packaging boundaries
Product availability statement
This equipment entry supports both stand-alone structures and integrated packages, including steel silo for sale listings tied to a defined scope boundary (structure only) or a system boundary (structure + transfer + dust control + packaging interfaces).
For crude, natural oil, and gas-related storage tank applications under API 650, refer to API 650, Natural Oil and Gas Storage Tanks.

Project-Ready Supply: What Octal Controls Beyond the Steel Silo Structure
Octal positions its China steel silo scope as an acceptance-ready supply package, not just fabricated steel. Steel silo structures, silo system modules, and related liquid tanks can be released under one boundary with interface lists that match how EPC and plant teams review equipment. Each shipment is organized so receiving can be closed by item and lot: packing lists map to equipment IDs, and marking/protection is applied for key interfaces to reduce site damage and “missing identity” NCRs. For system packages, Octal aligns transfer and dust-control equipment (dust collector, conveying/lifting, discharge/pneumatic interfaces, valves, and packaging/export modules) to the defined throughput and material behavior so the silo does not become a standalone bottleneck. Configuration is built around project inputs—capacity, diameter, material flow-ability/abrasion, enclosure and dust targets (including fly ash compliance cases), automation scope, and packaging mode—so the delivered scope matches the specification rather than requiring rework after arrival. After delivery, Octal supports spare parts and interface troubleshooting to keep commissioning and ongoing operation stable.
FAQ
Q1: What capacity range does a China steel silo typically cover, and what diameter range is common?
A1: Typical project coverage for a China steel silo in this equipment entry is 100–20,000 m³ with common diameters from φ3 m to φ35 m, with final sizing driven by material bulk density, buffer time, and site constraints.
Q2: How do I choose between spiral, welded, and bolt assembly in a China steel silo scope?
A2: China steel silo selection typically follows site logistics and the quality plan: spiral for efficient site assembly at larger capacities, welded for weld procedure/inspection control, and bolt assembly for transport/phased installation where sealing and bolt management are part of acceptance.
Q3: What should be included in a silo system solution beyond the steel silo structure?
A3: A complete silo system solution typically includes dust control (silo dust collector), conveying/lifting (belt conveyor or bucket elevator), discharge/transfer modules (air chute, silo pump, inflation equipment as applicable), control/sealing interfaces (valves), and packaging/export options such as a ton bag packaging machine.
Q4: Which industry systems are most common for steel silo projects, and what are the key control points?
A4: Common systems include petroleum coke, fly ash, slag powder, alumina, PVC granule, building materials, grain, mining, logistics transfer, and lithium ion battery production lines; key control points usually focus on dust containment, discharge stability, interface sealing, automation scope, and documentation/traceability for acceptance.